Level Up Your Photoshop Color-How to refine with Hue/Saturation and Selective Color
How to use Color Balance, Hue/Saturation, and Selective Color
In Adobe Photoshop, Color Balance, Hue/Saturation and Selective Color are powerful tools used to adjust and modify colors in an image. Here’s how each tool works and their key differences:
Color Balance
- How to Use:
Go to Image > Adjustments > Color Balance.
You can adjust the color tones using sliders for Shadows, Midtones, and Highlights. Each tone has three sliders: Cyan/Red, Magenta/Green, and Yellow/Blue.
Purpose: This tool lets you change the overall color balance by adjusting the amounts of primary colors in the image.
Best For: Correcting color casts and achieving more natural-looking tones. It’s useful for warming up or cooling down an image (for example, making a photo look more sunset-like or colder).
Limitations: You don’t have specific control over individual colors, only over tonal ranges (shadows, mid-tones, and highlights).
Hue/Saturation
How to Use
Go to Image > Adjustments > Hue/Saturation or use it as an adjustment layer (Layer > New Adjustment Layer > Hue/Saturation).
Use the Hue slider to shift all colors, the Saturation slider to increase or decrease color intensity, and the Lightness slider to make the image lighter or darker.
You can also target specific colors (e.g., only adjusting the Reds, Greens, or Blues) from the drop-down menu.
Purpose: It’s designed to globally or selectively shift colors and control their intensity.
Best For: Altering the overall color mood of an image, such as making colors more vivid or adjusting specific tones like desaturating a single color while keeping others vibrant.
Limitations: It lacks the fine-tuning that you can achieve with tools like Selective Color, as changes apply more broadly across selected color ranges.
Selective Color
How to Use:
Go to Image > Adjustments > Selective Color.
From the drop-down menu, choose a color family (e.g., Reds, Yellows, Greens, etc.).
Adjust the Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black (Key) sliders to fine-tune the color’s makeup.
Purpose: Selective Color gives you precise control over individual color channels, allowing you to fine-tune specific hues without affecting other parts of the image.
Best For: Adjusting specific colors in the image while maintaining control over the color composition. For example, tweaking skin tones, correcting color casts in specific areas, or altering certain hues without impacting the entire image.
Limitations: It’s more intricate than Hue/Saturation and requires a good understanding of how colors interact (CMYK adjustments).
Key Differences:
Color Balance adjusts broad tonal ranges and is great for fixing color casts or changing the overall warmth or coolness of an image.
Hue/Saturation controls overall or selective color intensity and hue shifts, affecting the entire image or specific color ranges.
Selective Color provides the most precise color control, letting you alter the composition of specific colors in a nuanced way.
Each tool serves a different purpose depending on how detailed or broad you want your color adjustments to be.
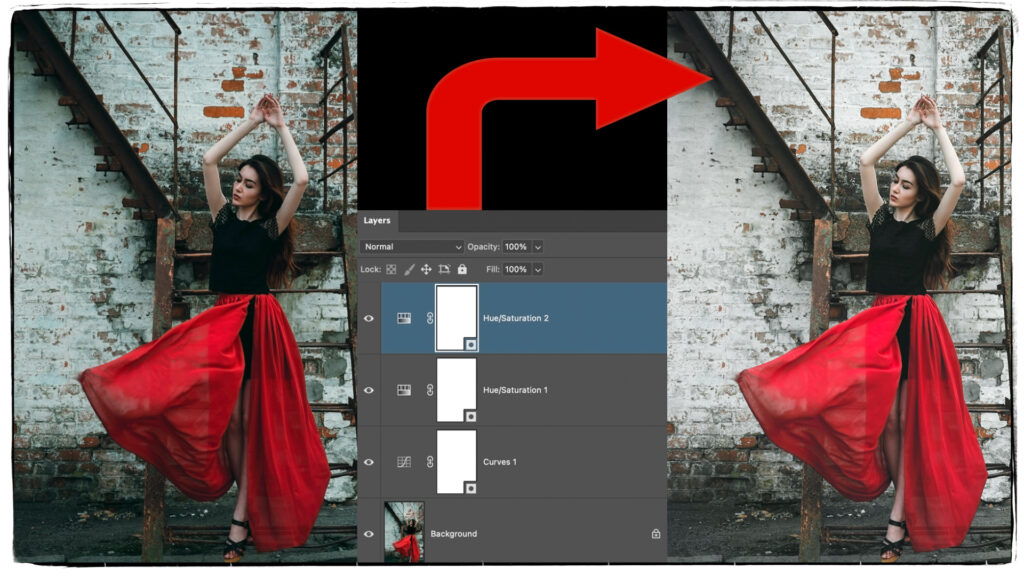
Hue/Saturation Layer Adjustment
In the image below, I use two different Hue/Saturation layer adjustments. The first one removed the cyan/blue cast in the background, and the second corrected for an oversaturation of red. Red is a difficult color to deal with in digital photography. It can easily become neon, and does not usually reflect the original color.
Creating Masks with a Fill of the Opposite Color
Another way to create a layer mask in Adobe Photoshop is to fill a selection with the opposite color of the mask. It might seem counterintuitive, but this techinque I use in this video is very helpful at times. Last of all I show you how to duplicate masks and move them to other layers.